Introduction:
Fermented cereal-based products have been a dietary staple in Asia for thousands of years. They are prepared by soaking, grinding, and fermenting cereal grains, and are known for their unique flavors, textures, and health-promoting properties. Fermentation not only transforms the taste and texture of cereal-based foods, but it also increases the bioavailability of nutrients and enhances their health-promoting properties. In this blog, we will explore the health-promoting constituents of Asian fermented cereal-based products in greater detail.
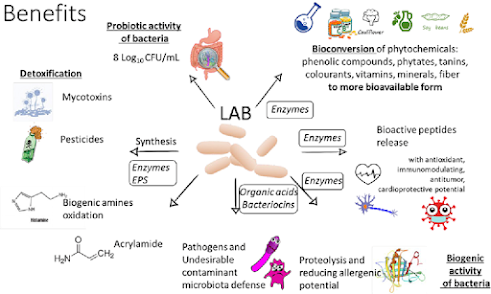
Probiotics:
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that help maintain a healthy gut microbiota. They improve digestion, boost immunity, and reduce the risk of gastrointestinal diseases. Fermented cereal-based products are a rich source of probiotics, with many traditional Asian dishes containing high levels of these beneficial bacteria. For example, Korean kimchi is a fermented vegetable dish made with cabbage, radish, and a variety of spices, including garlic, ginger, and chili. It is a popular side dish in Korean cuisine and is known for its sour and spicy flavor. Kimchi is an excellent source of probiotics, with over 200 different bacterial species present in a single serving. Another fermented cereal-based product that contains probiotics is Japanese natto. Natto is made from fermented soybeans and has a sticky, slimy texture and a pungent odor. It is a traditional breakfast food in Japan and is rich in the probiotic bacteria Bacillus subtilis. Chinese pickles, which are made by fermenting vegetables such as cucumber, radish, and cabbage, are also a good source of probiotics.
Antioxidants:
Antioxidants are compounds that protect the body against oxidative stress and inflammation, both of which can lead to chronic diseases such as cancer, cardiovascular disease, and diabetes. Fermented cereal-based products are a rich source of antioxidants, with many traditional Asian dishes containing high levels of these health-promoting compounds. For example, Indonesian tempeh is a fermented soybean cake that is rich in antioxidants such as isoflavones and saponins. Korean doenjang, a fermented soybean paste, is also rich in antioxidants, including phenolic compounds and isoflavones. Chinese fermented black beans, which are made by fermenting soybeans with salt and spices, are another example of a fermented cereal-based product that is rich in antioxidants.
Vitamins and Minerals:
Fermented cereal-based products are a good source of vitamins and minerals. The fermentation process increases the bioavailability of nutrients, making them easier to absorb and utilize by the body. Many traditional Asian dishes made with fermented cereal grains are rich in essential vitamins and minerals. For example, Indian idli is a fermented rice and lentil cake that is rich in vitamins B1, B2, B3, and B6, as well as minerals such as iron and calcium. Korean makgeolli, a traditional rice wine, is rich in vitamins B1, B2, and B6, as well as minerals such as magnesium and potassium. Japanese miso, a fermented soybean paste, is also rich in vitamins and minerals, including vitamin K, magnesium, and zinc.
Prebiotics:
Prebiotics are dietary fibers that promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. They improve digestion, boost immunity, and reduce the risk of gastrointestinal diseases. Fermented cereal-based products also contain prebiotics, making them an excellent addition to a healthy diet. For example, Chinese rice wine, also known as huangjiu, is a fermented cereal-based beverage made from rice, wheat, or barley. It is rich in prebiotic fibers such as oligosaccharides and beta-glucans, which promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria. Indian dosa, a fermented rice and lentil crepe, is another example of a fermented cereal-based product that contains prebiotics. The fermentation process breaks down the carbohydrates in the rice and lentils, creating prebiotic fibers that promote the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Bioactive Peptides:
Bioactive peptides are small protein fragments that have health-promoting properties. They have been shown to have antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial effects, among others. Fermented cereal-based products are a good source of bioactive peptides, with many traditional Asian dishes containing high levels of these health-promoting compounds. For example, Korean doenjang is rich in bioactive peptides such as angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors, which help lower blood pressure. Japanese natto is also rich in bioactive peptides, including nattokinase, which has been shown to have anticoagulant and fibrinolytic effects.
Conclusion:
Fermented cereal-based products are a dietary staple in Asia and are known for their unique flavors, textures, and health-promoting properties. They are a rich source of probiotics, antioxidants, vitamins, minerals, prebiotics, and bioactive peptides, all of which contribute to their health-promoting properties. Incorporating fermented cereal-based products into your diet can help improve digestion, boost immunity, reduce the risk of chronic diseases, and promote overall health and well-being. So why not try adding some traditional Asian fermented dishes to your next meal? Your taste buds and your body will thank you.
Comments
Post a Comment